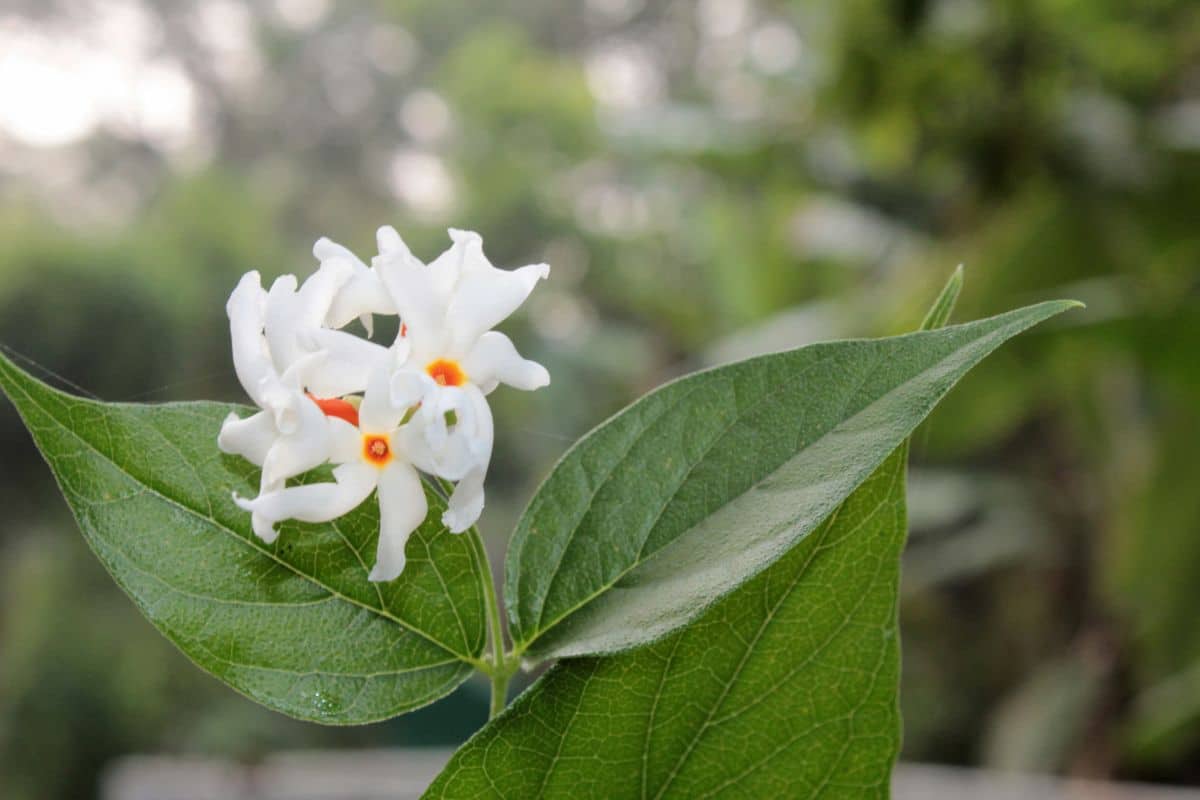
Night-blooming jasmine transforms gardens into aromatic sanctuaries when evening shadows fall. This remarkable flowering plant releases its intoxicating fragrance after sunset, creating magical moments for gardeners who appreciate nocturnal beauty. Understanding proper cultivation techniques ensures your night blooming jasmine plant thrives while delivering spectacular evening performances season after season.
The enchanting Epiphyllum oxypetalum and Cestrum nocturnum varieties represent the most popular night-blooming jasmine species. These tropical beauties demand specific growing conditions that mirror their native habitats. Success depends on providing adequate warmth, humidity, and strategic placement within your garden or indoor growing space.
Understanding night blooming jasmine varieties and characteristics
Several distinct species carry the night blooming jasmine designation, each offering unique growing requirements and flowering patterns. The queen of the night (Epiphyllum oxypetalum) produces enormous white blooms that unfurl dramatically after darkness settles. This epiphytic cactus requires well-draining soil and filtered sunlight during daylight hours.
Cestrum nocturnum, commonly called lady of the night, develops clusters of small tubular flowers that emit powerful fragrances. This shrub-like variety tolerates various soil conditions while preferring partial shade environments. Understanding these differences helps gardeners select appropriate varieties for their specific climate zones and growing conditions.
The blooming cycle creates spectacular overnight displays that last mere hours. Most varieties open their petals between sunset and midnight, then close permanently before dawn breaks. This ephemeral nature makes timing crucial for gardeners wanting to witness the full blooming spectacle.
Temperature sensitivity affects flowering schedules significantly across different regions. Warmer climates encourage more frequent blooming cycles, while cooler areas may experience sporadic flowering patterns. Like caring for other sensitive plants such as how to look after moth orchids, maintaining consistent environmental conditions proves essential for optimal flowering performance.
Light requirements vary between species but generally favor bright, indirect sunlight during daytime hours. Direct afternoon sun can scorch delicate foliage, while insufficient light reduces flowering potential significantly. Strategic positioning near east-facing windows or under filtered outdoor shade creates ideal growing conditions.
Optimal growing conditions and soil requirements
Creating the perfect growing environment begins with understanding soil composition preferences for night-blooming jasmine varieties. Well-draining, slightly acidic soil with pH levels between 6.0 and 7.0 supports healthy root development. Heavy clay soils retain excessive moisture, leading to root rot problems that devastate these sensitive plants.
Incorporating organic matter improves soil structure while providing essential nutrients gradually. Compost, aged manure, and leaf mold create nutrient-rich growing mediums that retain appropriate moisture levels without becoming waterlogged. Sandy loam mixtures offer excellent drainage characteristics ideal for most jasmine varieties.
Container growing requires specific potting mix formulations that balance drainage with moisture retention. Commercial cactus or succulent mixes work excellently for epiphytic varieties, while standard potting soil amended with perlite suits shrub-type jasmines perfectly.
The following soil amendments enhance growing conditions significantly :
- Perlite or pumice for improved drainage
- Coconut coir for moisture retention
- Worm castings for gentle fertilization
- Pine bark chips for organic matter
- Coarse sand for structural support
Humidity levels between 50-70% create optimal growing atmospheres for these tropical plants. Indoor growers benefit from using humidity trays, room humidifiers, or grouping plants together to increase local moisture levels. Outdoor cultivation in arid regions requires strategic placement near water features or frequent misting schedules.
Temperature stability proves crucial for consistent flowering performance. Most varieties prefer temperatures between 65-80°F during growing seasons, with slight cooling at night triggering blooming responses. Sudden temperature fluctuations stress plants and reduce flowering frequency significantly. Similar to specialized care requirements for what fertilizer for swiss cheese plant, consistent environmental conditions promote healthy growth patterns.
Watering techniques and seasonal care management
Mastering watering schedules determines success or failure with night-blooming jasmine cultivation. These plants require consistent moisture without waterlogged conditions that promote fungal diseases. Deep, infrequent watering encourages robust root systems while preventing surface root development that makes plants vulnerable to drought stress.
Spring and summer growing seasons demand increased watering frequency as plants actively develop new growth and prepare for flowering cycles. Check soil moisture levels regularly by inserting fingers two inches deep into growing medium. Water thoroughly when upper soil layers feel dry but deeper layers retain slight moisture.
Winter dormancy periods require dramatically reduced watering schedules to prevent root rot during cooler temperatures. Many varieties enter semi-dormant states where growth slows significantly. Reducing watering frequency to every two weeks or monthly prevents soil saturation while maintaining plant health.
Morning watering schedules allow plants to absorb moisture throughout daylight hours while reducing nighttime humidity that encourages fungal problems. Avoid watering directly onto foliage, especially during evening hours when plants prepare for blooming cycles. Soil-level irrigation methods prevent water spots on leaves while maintaining appropriate root zone moisture.
Seasonal fertilization supports healthy growth and abundant flowering throughout active growing periods. Balanced liquid fertilizers applied monthly during spring and summer provide essential nutrients without overwhelming root systems. Phosphorus-rich formulations encourage blooming, while nitrogen supports foliage development. Understanding proper misting techniques, similar to does swiss cheese plant like to be misted, helps maintain optimal humidity without creating disease-prone conditions.
Pruning requirements remain minimal for most night-blooming jasmine varieties. Remove dead or damaged growth promptly to prevent disease spread. Light shaping after flowering seasons maintains attractive plant forms without sacrificing next season’s blooming potential. Avoid heavy pruning that removes flowering shoots and reduces overall plant vigor significantly.
Troubleshooting common problems and maximizing blooms
Successful night jasmine cultivation requires identifying and addressing common growing challenges before they compromise plant health. Yellowing leaves often indicate overwatering, nutrient deficiencies, or inadequate drainage conditions. Adjusting watering schedules and improving soil drainage typically resolves these issues quickly when caught early.
Pest management focuses on preventing infestations rather than treating established problems. Spider mites, aphids, and scale insects attack stressed plants more frequently than healthy specimens. Regular inspection and immediate treatment with insecticidal soaps or horticultural oils control minor infestations effectively without harsh chemical interventions.
Blooming failure frustrates many growers who provide excellent care but see few flowers. Temperature fluctuations, insufficient darkness periods, or excessive nitrogen fertilization commonly cause blooming problems. Night-blooming varieties require true darkness during evening hours to trigger flowering responses properly.
Light pollution from street lamps or indoor lighting disrupts natural blooming cycles significantly. Positioning plants away from artificial light sources or providing blackout periods encourages consistent flowering patterns. Some varieties bloom only once annually, while others produce multiple flowering cycles throughout growing seasons.
Disease prevention through proper cultural practices eliminates most fungal and bacterial problems before symptoms appear. Adequate air circulation, appropriate watering techniques, and prompt removal of diseased plant material maintain healthy growing environments. Quarantining new plants prevents introducing diseases to established collections.
Maximizing fragrance intensity requires understanding optimal growing conditions that promote essential oil production. Slight water stress before blooming periods concentrates aromatic compounds within flower tissues. However, severe drought stress prevents blooming entirely, requiring careful balance between adequate moisture and controlled stress applications.