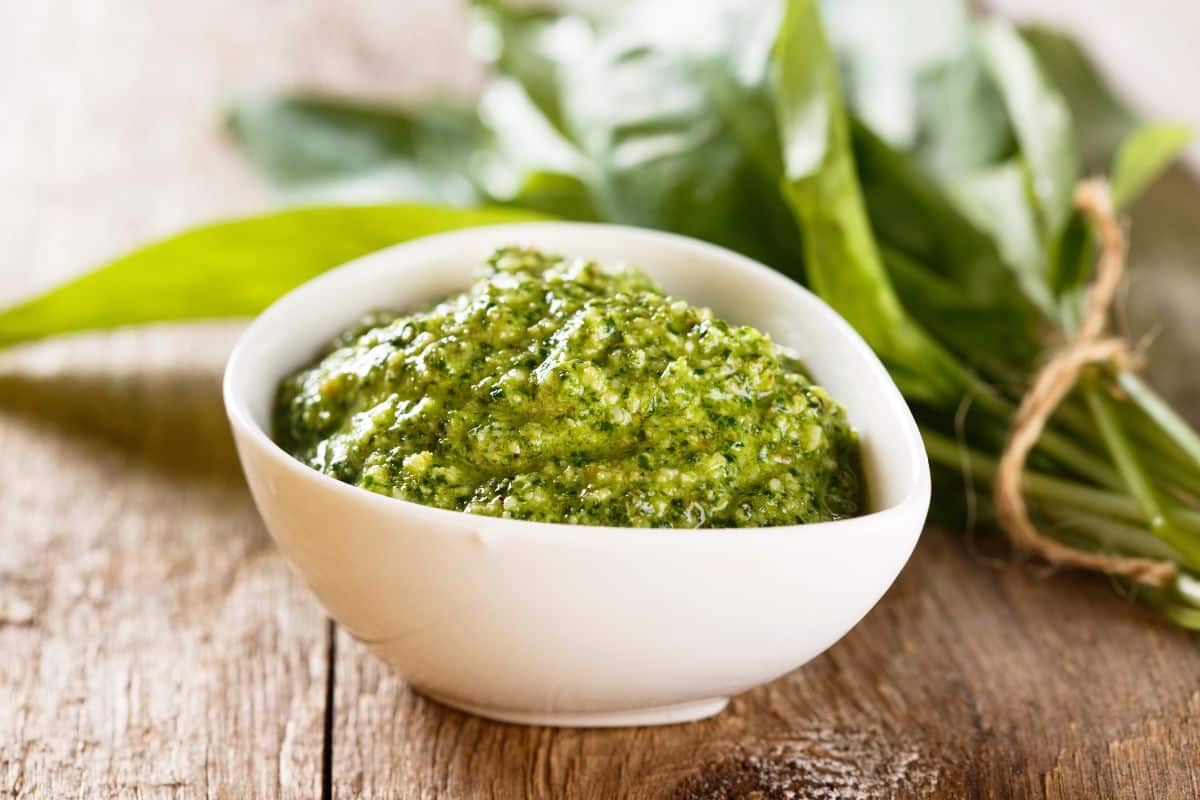
Pesto sauce brings a burst of flavor to countless dishes, from pasta to sandwiches. With its vibrant green color and aromatic profile, many wonder about its nutritional value. Let’s explore what nutrition experts say about this popular Italian condiment and whether it deserves a place in a healthy diet.
Nutritional profile of traditional pesto
Traditional pesto Genovese combines basil leaves, pine nuts, Parmesan cheese, garlic, olive oil, and salt. This classic combination creates a sauce rich in both flavor and nutrients. Each ingredient contributes unique health benefits that together make pesto more than just a tasty addition to meals.
Fresh basil serves as the foundation of authentic pesto and provides numerous health advantages. This aromatic herb contains essential vitamins like K, A, and C, along with minerals such as manganese, calcium, and iron. Basil also contains powerful antioxidants that help combat oxidative stress in the body.
Olive oil, another key component, delivers heart-healthy monounsaturated fats. These fats may help reduce inflammation and decrease the risk of heart disease when consumed as part of a balanced diet. Extra virgin olive oil offers the most health benefits due to its minimal processing and higher antioxidant content.
Pine nuts contribute protein, healthy fats, and essential minerals like magnesium, zinc, and iron. Though calorie-dense, they provide satisfying nutrients that support overall health. Parmesan cheese adds calcium for bone health, while garlic offers immune-boosting compounds like allicin.
A typical two-tablespoon serving of traditional pesto contains approximately:
- 160-200 calories
- 16-18 grams of fat
- 4-6 grams of protein
- 2-3 grams of carbohydrates
- 200-300 mg of sodium
Health benefits of pesto ingredients
The individual components of pesto each contribute valuable nutrients that support various aspects of health. Basil, the star ingredient, contains powerful plant compounds including eugenol, linalool, and rosmarinic acid. These compounds have demonstrated anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties in research studies.
Olive oil provides polyphenols and oleic acid that may help reduce inflammation and protect against chronic diseases. Regular consumption of olive oil has been linked to improved heart health and reduced risk of certain cancers. The Mediterranean diet, which features olive oil prominently, consistently ranks among the healthiest eating patterns worldwide.
Pine nuts contain pinolenic acid, which some studies suggest may help suppress appetite and support weight management. They also provide vitamin E, which acts as an antioxidant in the body. While garlic adds distinctive flavor, it simultaneously delivers compounds that may help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Even the Parmesan cheese in pesto offers nutritional benefits beyond calcium. It contains high-quality protein and vitamin B12, which supports nervous system function and energy production. For those concerned about dairy consumption, nutritionists note that the amount of cheese in a typical serving of pesto is relatively small.
Choosing organic ingredients for homemade pesto can further enhance its health profile by reducing exposure to pesticides and other chemicals. This is particularly important for basil, as leafy herbs can sometimes contain residual agricultural chemicals when grown conventionally.
Potential nutritional concerns
Despite its nutritional merits, pesto does present some considerations for those monitoring specific aspects of their diet. The calorie and fat content can be significant relative to the small serving size typically used. While most of these fats are the healthy unsaturated variety, they still contribute to overall calorie intake.
Sodium levels in commercial pesto sauces often exceed those in homemade versions. Many store-bought options contain between 250-400mg of sodium per serving, which can be concerning for individuals managing hypertension or heart conditions. Making sauces at home allows better control over sodium content.
Those with nut allergies should exercise caution with traditional pesto containing pine nuts. However, nutritionists suggest several alternatives that maintain the sauce’s nutritional profile while eliminating allergen concerns:
- Sunflower seeds offer similar texture and healthy fats
- Pumpkin seeds provide additional iron and protein
- Hemp seeds deliver omega-3 fatty acids
- Walnuts can substitute for pine nuts while adding omega-3s
For those limiting dairy, nutritional yeast can replace Parmesan cheese while adding B vitamins and a similar savory flavor. Leafy greens like kale or spinach can partially replace or supplement basil to increase the nutrient density while reducing cost.
Individuals following specific dietary patterns may need to adapt traditional pesto recipes. Vegan versions might substitute nutritional yeast for cheese, while low-carb diets might enjoy pesto as a flavorful fat source when limiting pasta consumption.
Incorporating pesto into a healthy diet
Nutritionists generally agree that pesto can be part of a balanced eating pattern when consumed mindfully. The key lies in appropriate portion sizes and creative serving methods that maximize flavor while managing calorie intake.
Rather than using pesto solely on pasta, consider these nutritionist-approved applications:
Spread a thin layer on sandwiches with fresh sprouts instead of mayonnaise to add flavor with fewer calories. Mix a spoonful into vegetable soups to enhance taste without significantly increasing the calorie content. Use as a marinade for grilled vegetables or lean proteins to add Mediterranean flair to meals.
For those monitoring fat intake, diluting pesto with a bit of the cooking water from pasta can create a lighter sauce that coats food more efficiently. This technique stretches the pesto further while reducing calories per serving.
Making homemade pesto allows complete control over ingredients and proportions. Increasing the ratio of basil to oil creates a more herb-forward sauce with fewer calories. Choosing organic ingredients ensures the highest quality nutrients without unwanted chemicals.
When purchasing commercial pesto, nutritionists recommend reading labels carefully. Look for products with minimal additives and preservatives. Some brands now offer reduced-oil or reduced-sodium versions that maintain flavor while addressing nutritional concerns.
The verdict from nutrition experts? Pesto can absolutely be part of a healthy diet when used thoughtfully as a flavorful addition to nutrient-dense foods. Its combination of plant-based ingredients and beneficial compounds makes it a more nutritious choice than many other condiments and sauces.